Kidney Diseases
Know More About Our Sub-Specialization
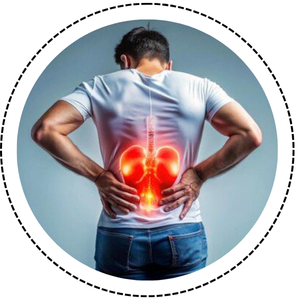
- Kidney infections occur when bacteria spread from the bladder to the kidneys.
- They can cause pain in the lower back or sides, fever, chills, and frequent urination.
Common causes include untreated urinary tract infections (UTIs). - Drinking plenty of water and maintaining good hygiene help prevent them.
- Prompt antibiotic treatment is important to avoid kidney damage.
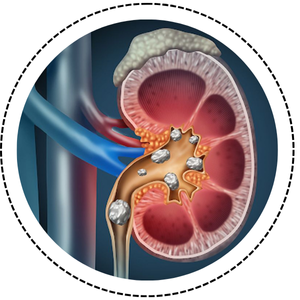
- Kidney stones are hard mineral deposits that form inside the kidneys.
- They can cause severe pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen.
- Common causes include dehydration, high salt intake, and certain medical conditions.
- Small stones may pass naturally, while larger ones may need medical treatment.
- Drinking plenty of water helps prevent kidney stones from forming.
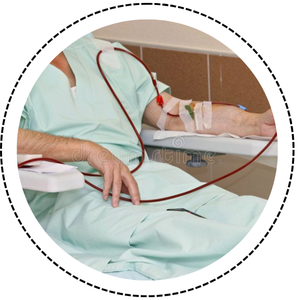
- Dialysis is a treatment for patients whose kidneys can no longer filter waste from the blood.
- It helps remove excess fluids, salts, and toxins from the body.
- There are two main types: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
- Patients often need dialysis several times a week to stay healthy.
- Maintaining a proper diet and following medical advice is crucial for dialysis patients.
Contact Form
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Kidney diseases are conditions in which the kidneys are unable to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood effectively, affecting overall body balance and health.
Symptoms can include swelling in the legs or face, changes in urine output or color, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, or high blood pressure.
Common causes include diabetes, high blood pressure, infections, kidney stones, prolonged medication use, and genetic factors.
Diagnosis usually involves blood tests, urine tests, imaging studies, and clinical evaluation to assess kidney function.
Yes. Early diagnosis, proper treatment, lifestyle changes, and regular follow-ups can slow disease progression and help maintain kidney health.
