Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic condition that affects how the body uses blood sugar (glucose).
- It occurs when the body produces little or no insulin or cannot use it effectively.
- There are mainly two types — Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
- Common symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
- Proper diet, exercise, and medication help manage blood sugar and prevent complications.
Know More About Our Sub-Specialization
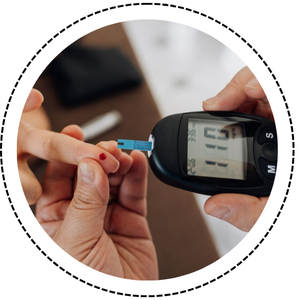
- The Defeat Diabetes Program promotes natural diabetes prevention and reversal.
- It focuses on a whole-food, plant-based diet.
- Encourages regular exercise and healthy habits.
- Teaches blood sugar and lifestyle management.
- Empowers people to take control of their health.
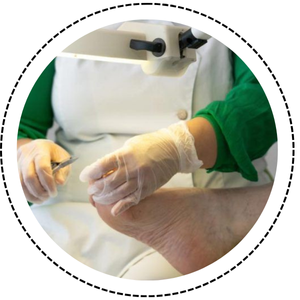
- Diabetes foot care is essential to prevent infections and complications.
- Check your feet daily for cuts, blisters, or swelling.
- Keep them clean, dry, and moisturized, avoiding between the toes.
- Always wear comfortable and protective footwear.
- Visit a doctor or podiatrist regularly for foot check-ups.
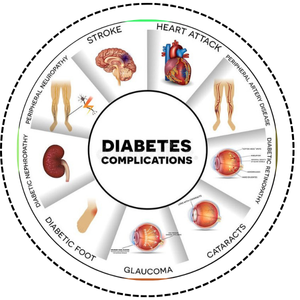
- Diabetes can cause serious complications if not managed properly.
- It may damage the kidneys, leading to kidney disease or failure.
- The heart and blood vessels can be affected, increasing heart disease risk.
- Nerve damage may cause pain, numbness, or poor circulation.
- It can also harm the skin and eyes, leading to infections and vision problems.

- Diabetic nutrition focuses on managing blood sugar through healthy eating.
- Meals should include whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of vegetables.
- Limit sugar, refined carbs, and saturated fats.
- Eat smaller, balanced meals at regular intervals.
- Stay hydrated and monitor food portions to maintain stable glucose levels.
Contact Form
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Symptoms may include frequent urination, excessive thirst, increased hunger, unexplained weight changes, fatigue, slow-healing wounds, or blurred vision.
Yes. With proper medication, regular monitoring, a healthy diet, physical activity, and medical supervision, diabetes can be effectively controlled.
Diabetes is usually a long-term condition, but with good management, patients can lead healthy and active lives and prevent complications.
Regular blood sugar monitoring, routine checkups, lifestyle management, and early treatment of changes help reduce the risk of complications.
